Where in the World Are the CWB Clowns?!
Nothing Stops a CWB Performance!
Well, almost nothing! We’ve forded rivers carrying our props above our head just to make it to a show we promised to give. When we’re invited, our goal is always to get to YES. We work closely with our partners to address any ethical and security concerns so that our performances can take place, even in challenging circumstances.
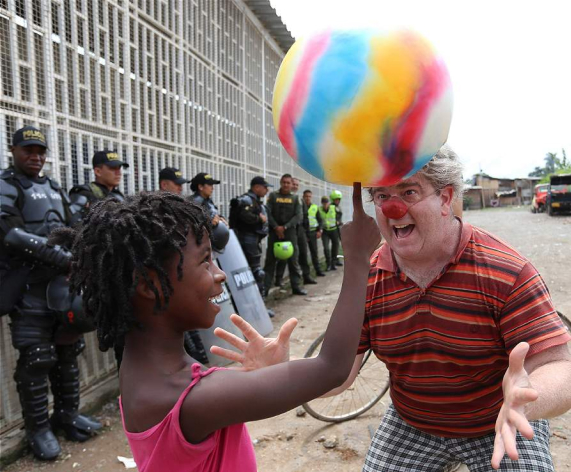





The Bottom Line: We Cross Borders of ALL Kinds!
As clowns, we’re used to pushing the boundaries and playing the trickster. Through intentional humor, we both question power dynamics and bring people together — and art imitates life!
As we travel the world, we erase boundaries of all kinds, not just global borders.
Even in the same tour, we might put on shows for the children of gang members, the children of police officers, and the children of guerrilla fighters. We perform for the children of hurricanes, of war, of displacement, of disputed borders, and of human rights abuses.
Kids are kids, and because we’re politically neutral, we clown for them just the same.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does CWB decide where to go?
CWB goes where invited. We work with community partners to evaluate if we’ll truly meet the needs of our audiences. We’ve seen clowning have a positive impact in many situations, but respect that some communities might not want us to visit.
Why don’t CWB clowns wear makeup or wigs?
CWB is part of a contemporary circus movement with minimal makeup. The goal is to emphasize the clown’s recognizable humanity. Often CWB performers will wear a red nose and use minimal make-up to highlight their eyes, lips and cheeks. Since we are often performing in close proximity to our audiences, more makeup could be overwhelming.
I’m a clown. Can I perform with you?
That depends. What type of clown are you? Clowns Without Borders (CWB) artists are contemporary circus performers who work in ensemble. The clown qualities we treasure are vulnerability, authenticity, and presence. We work with artist who use non-verbal storytelling, physical comedy, and circus skills. Face-painting, rainbow wigs and balloon-twisting are lots of fun, but not what we do. See our featured artist page to learn more.
Is there anywhere you won’t perform?
Due to the devastating history of Orphanage Trafficking (children being trafficked and sold to orphanages to support voluntourism programs), we rarely work in orphanages.
Have another question? Reach out any time!